Pneumothorax Treatment: Comprehensive Insights and Approaches
Pneumothorax is a condition marked by the accumulation of air in the pleural space, which can lead to the collapse of a lung. The treatment of pneumothorax is crucial as it can significantly affect breathing and overall health. Understanding the intricacies of pneumothorax treatment is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Understanding Pneumothorax
Before diving into treatment options, it’s important to understand the basics of pneumothorax. This condition can occur spontaneously, due to trauma, or as a result of medical procedures. The symptoms typically include:
- Sudden sharp chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing and increased heart rate
- Cyanosis (bluish color of skin due to low oxygen)
Types of Pneumothorax
There are several types of pneumothorax, each requiring different treatment approaches:
- Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Often occurs in young, tall, and thin individuals without any apparent cause.
- Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Associated with underlying lung diseases such as COPD or cystic fibrosis.
- Traumatic Pneumothorax: Results from chest injuries, such as fractures or penetrating wounds.
- Iatrogenic Pneumothorax: Occurs due to medical interventions, such as lung biopsies or mechanical ventilation.
Diagnosis of Pneumothorax
A proper diagnosis of pneumothorax is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals utilize a variety of methods to diagnose this condition, including:
- Physical Examination: Doctors will listen for abnormal lung sounds and check for signs of respiratory distress.
- Imaging Tests: Chest X-rays and CT scans are critical in visualizing air in the pleural space.
- Ultrasound: Increasingly used in emergency settings to quickly assess the presence of a pneumothorax.
Pneumothorax Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, the treatment of pneumothorax varies depending on the severity and underlying cause. Here are the primary approaches:
Observation
In cases of small pneumothorax with minimal symptoms, a conservative approach may be taken. The air in the pleural space often reabsorbs on its own without intervention. This strategy includes:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Monitoring symptoms closely
- Implementing breathing exercises to improve lung function
Needle Decompression
For moderate pneumothorax or cases with significant respiratory distress, a procedure known as needle decompression may be necessary. This involves:
- Inserting a large-bore needle into the chest wall to release trapped air.
- Temporary relief of symptoms while further treatment is sought.
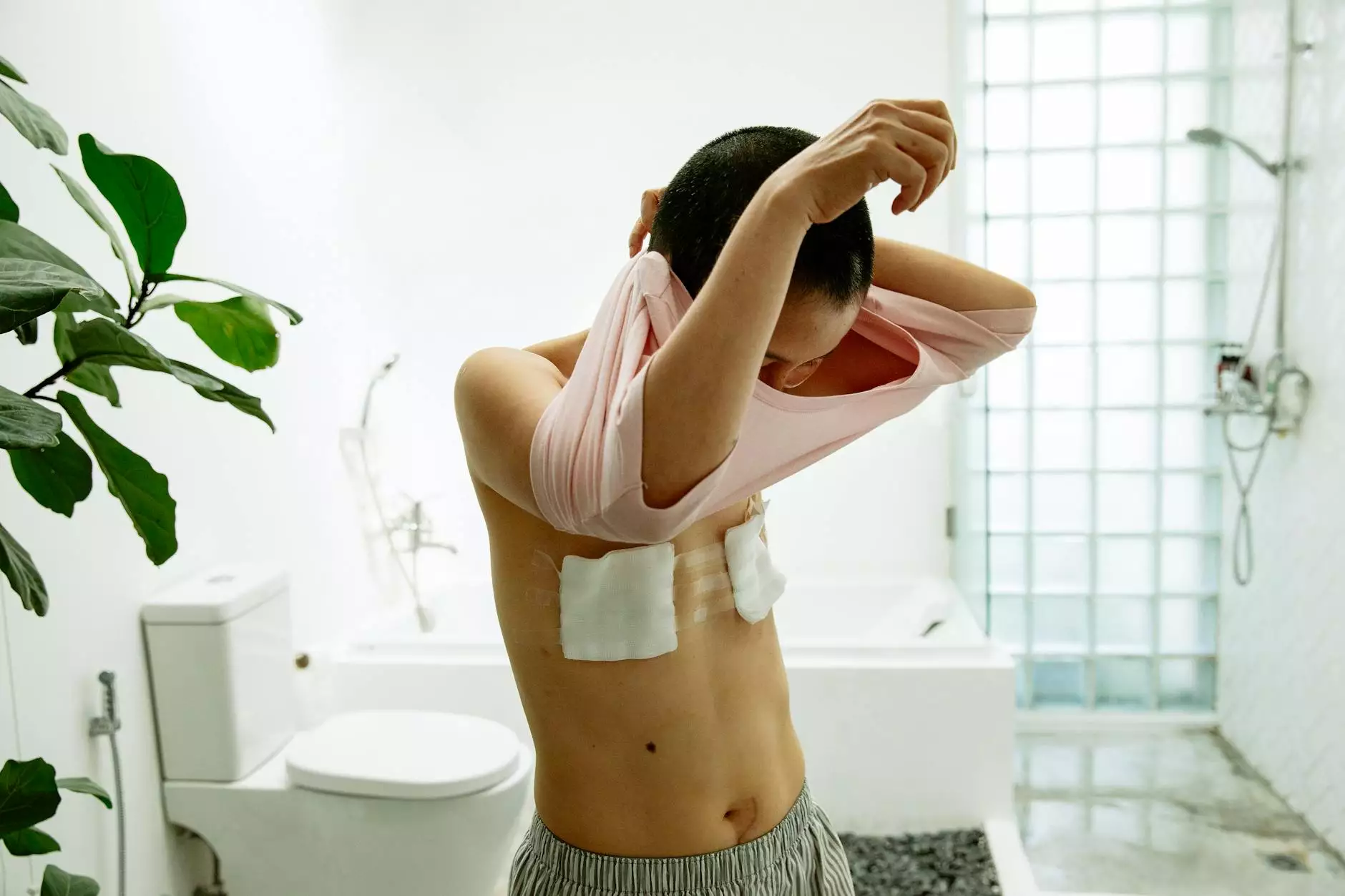
Chest Tube Insertion
For larger pneumothoraces or persistent cases, the insertion of a chest tube is often required. This procedure includes:
- A tube is placed through the chest wall into the pleural space to drain air.
- It helps the lung re-inflate and restores normal breathing function.
Surgery
In some cases, particularly with recurrent pneumothorax, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options involve:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive procedure to repair blebs or lung tissues.
- Open Thoracotomy: More extensive surgery used as a last resort for severe cases.
Post-Treatment Care
After treatment, careful monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure complete recovery. Key aspects of post-treatment care include:
- Chest X-rays to verify lung re-expansion
- Gradual resumption of normal activities
- Avoiding air travel and flying until cleared by a healthcare provider
Role of Healthcare Professionals
The treatment of pneumothorax is not solely the responsibility of surgeons or specialists. A multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals is crucial:
- Primary Care Physicians: Often the first point of contact for patients experiencing symptoms.
- Emergency Physicians: Provide immediate care on presentation to the emergency department.
- Respiratory Therapists: Assist in optimizing pulmonary function during recovery.
Prevention of Pneumothorax
While not all cases of pneumothorax can be prevented, certain measures can reduce risk, particularly in individuals with underlying conditions. Preventative strategies include:
- Regular lung health assessments for those with chronic lung diseases.
- Avoiding smoking to reduce damage to lung tissues.
- Wearing appropriate protective gear during high-risk activities like extreme sports or construction work.
Conclusion
The management of pneumothorax treatment is a nuanced process that requires attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of the condition. Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention can significantly improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
For further information on pneumothorax treatment or to schedule a consultation, please visit Neumark Surgery.
pneumothorax treatment